Steel Pipe vs. HDPE Pipe – What Actually Matters in the Field
News 2026-01-27
Pipe selection looks clean on drawings.
In the field, problems show up later—after settlement, seasonal change, or years in service.
Steel pipe and HDPE pipe aren’t interchangeable.
They solve different problems and fail in different ways.
This comparison focuses on how each pipe behaves once conditions stop being ideal.
Steel Pipe and HDPE Pipe – What You’re Really Working With
Steel Pipe
Steel pipe is made from carbon or alloy steel.
It delivers strength through rigidity and carries load directly.
It’s typically used where failure isn’t acceptable:
-
High-pressure systems
-
Industrial and process piping
-
Structural or exposed installations
HDPE Pipe
HDPE pipe is made from high-density polyethylene.
It’s flexible, lightweight, and corrosion resistant.
Common applications include:
-
Water supply and drainage
-
Sewer systems
-
Underground utilities
Material choice defines how a pipe behaves once buried.
Where Steel and HDPE Handle Load Very Differently
Comparison of rigid steel pipe and flexible HDPE pipe load behavior underground
Most long-term failures come from misunderstood load behavior.
1. Steel Pipe – Strength Comes From Rigidity
Steel pipe resists load by staying stiff.
It limits deformation and maintains alignment under traffic and pressure.
That rigidity delivers predictable performance, especially when tolerances matter.
Steel pipe carries the load itself.
2. HDPE Pipe – Flexibility Shares the Load
HDPE pipe allows controlled deformation and relies on surrounding soil for support.
When bedding and compaction are done right, this works well.
When they aren’t, deformation accumulates quietly over time.
HDPE performance depends heavily on soil quality.
How Environment and Corrosion Change the Equation
1. Steel Pipe – Corrosion Control Is Non-Negotiable
Steel pipe doesn’t fail from lack of strength.
It fails when corrosion protection is underspecified.
In aggressive environments, steel systems require:
-
Coatings
-
Linings where needed
-
Cathodic protection
With proper protection, steel delivers long, predictable service life.
2. HDPE Pipe – Chemical Stability Built In
HDPE doesn’t rust and resists most soil and wastewater chemicals.
That makes it suitable for corrosive underground environments with limited access.
What Installation Really Looks Like on Site
1. Steel Pipe – Weight and Precision
Steel pipe requires lifting equipment, alignment control, and skilled labor.
Installation takes longer, but the result is a rigid system that stays put.
2. HDPE Pipe – Speed With Conditions
HDPE pipe is lightweight and fast to install.
Heat fusion creates continuous runs, but performance still depends on proper bedding.
Pressure and Temperature – Where Limits Matter
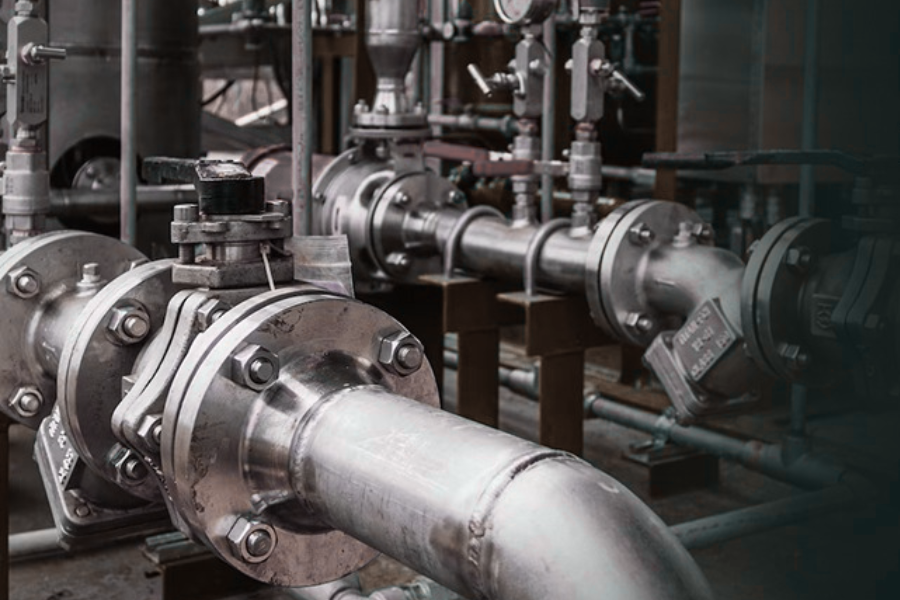

Steel pipe used in high-pressure and high-temperature industrial systems
1. Steel Pipe – Built for Extreme Conditions
Steel pipe handles high pressure and high temperature without loss of strength.
That’s why it remains standard for steam, oil, gas, and industrial fluids.
2. HDPE Pipe – Know the Thermal Ceiling
HDPE performs well under moderate pressure at ambient temperatures.
As temperature rises, stiffness and load capacity drop.
Ignoring this limit leads to long-term deformation.
Service Life and Cost Reality
Steel pipe requires corrosion management but offers predictable long-term performance.
HDPE needs minimal maintenance underground but depends on installation quality.
Lifecycle cost—not material price—should drive selection.
Where Each Pipe Type Makes Sense
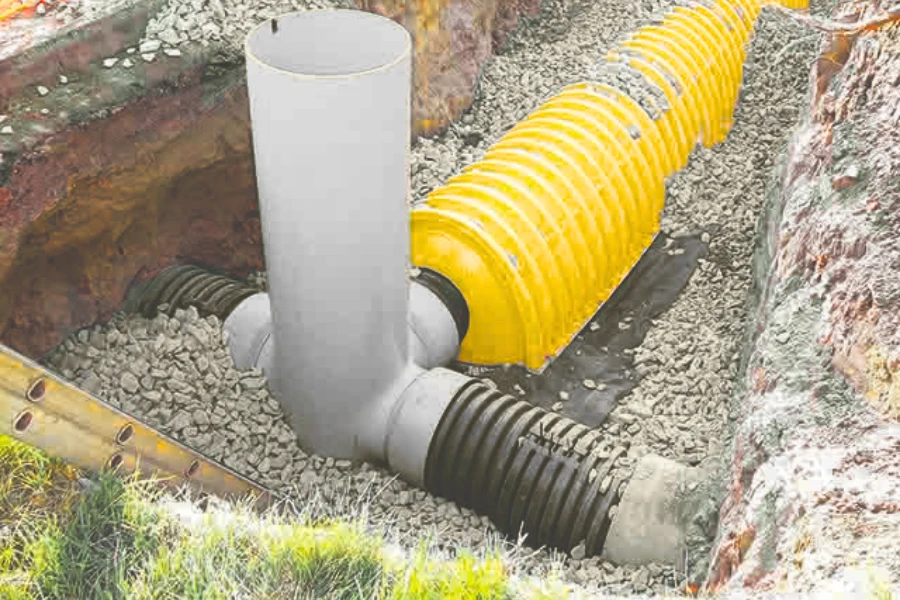

Typical applications of steel pipe and HDPE pipe in infrastructure projects
Steel pipe
-
High-pressure transmission
-
Industrial systems
-
Structural or exposed use
HDPE pipe
-
Water and drainage
-
Sewer systems
-
Underground utilities
The Right Pipe Depends on How the System Works
Steel pipe provides strength, pressure capacity, and structural certainty.
HDPE pipe offers flexibility, corrosion resistance, and installation efficiency underground.
Projects succeed when pipe selection matches real operating conditions, not convenience.
That’s why Ben-Thomas has focused for decades on metal culvert pipe production lines—because when steel is the right choice, consistency and manufacturing quality decide long-term performance.
Tools help build systems.
Experience and sound engineering decisions keep them working.
FAQ
Q: Is HDPE pipe suitable for high-pressure applications?
HDPE pipe handles moderate pressure well in water and drainage systems. However, steel pipe remains the standard for very high-pressure or high-temperature service. Oil, gas, steam, and industrial fluids require steel’s strength and thermal stability to maintain safety, alignment, and long-term reliability under extreme operating conditions.
Q: Does HDPE pipe last longer than steel pipe?
In corrosive or buried environments, HDPE pipe often achieves a longer effective service life because it does not rust. Steel pipe can also last decades, but only when coatings, linings, or cathodic protection are properly designed and maintained throughout the system’s operating life.
Q: Which pipe is better for underground installation?
HDPE pipe is commonly preferred underground due to its flexibility, corrosion resistance, and faster installation. Steel pipe can also be used below grade, but it requires corrosion protection and stricter control of bedding, alignment, and long-term inspection to ensure reliable performance.
Q: Are steel pipes harder to install than HDPE pipes?
Yes. Steel pipes are heavier and typically require lifting equipment, welding, and skilled labor. Installation takes more time and coordination. HDPE pipes are lightweight and use fusion joints, allowing faster installation and easier alignment, especially in long or curved underground runs.
Q: Can HDPE pipe replace steel pipe in all applications?
No. HDPE cannot replace steel in high-temperature, high-pressure, or structural applications. Steel remains essential where pressure, heat, or load tolerance is critical. Each material serves a different engineering role, and substitution without considering operating limits often leads to premature failure.
Q: Which pipe has lower maintenance requirements?
HDPE pipe generally requires less maintenance because it resists corrosion and most chemical attack. Steel pipe demands regular inspection and corrosion control. When protection systems are maintained correctly, steel performs reliably, but neglect increases long-term risk and maintenance cost.
Q: How do engineers decide between steel and HDPE pipe?
Engineers evaluate pressure, temperature, soil conditions, corrosion risk, installation constraints, and lifecycle cost. The decision focuses on how the pipe will behave in service over time, not on material preference. Correct selection reduces failures, maintenance, and long-term operational risk.



